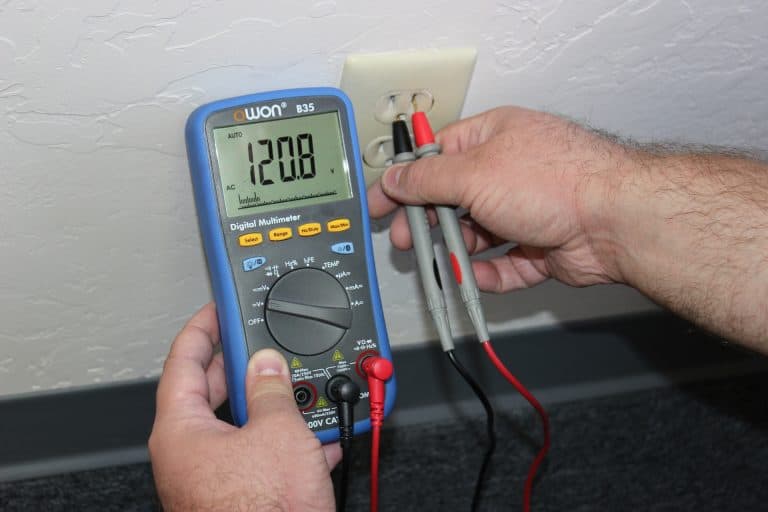
One of the most unpleasant aspects of owning a home is dealing with the electrical system. When an outlet stops working, one of the most typical concerns is that pinpointing the exact cause of the problem can be difficult. For example, you could have the circuit breaker on but no power to outlet for various reasons.
So before you call an electrician, read this article to understand the problem better and the best steps to take. We discovered common causes for an electrical outlet that isn't working throughout our investigation for this post, even if the breaker appears to be on.
Along with the frequent causes, we have elaborated simple solutions that most households can do without calling or paying an electrician. You may have a circuit breaker on, but no power to outlet and here are a few simple actions to take.
Steps:
1. Try Resetting the Breaker
First, ensure sure the breaker in question hasn't been tripped. Next, unplug all the devices connected to the breaker in question to do so. After that, reset the breaker by turning it off and on again. It will ensure that the breaker is turned on and that electricity is being delivered to the outlets. The problem is solved if you discover that electricity is now available through those outlets.
2. Make sure the GFCI Reset Button is Turned on
Check the GFCI reset button if your circuit breaker is on, but no power is coming through to its corresponding outlets. Ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs, often known as GFIs) are mini circuit breakers that can also cut power. Although this isn't always the case, you may have GFCI outlets if your home is modern.
How to Reset a GFCI
Let's say your breaker hasn't tripped, but you're experiencing a partial power outage, or a single electrical outlet isn't working. In either situation, the GFCI outlet is reset before power can be restored. It would be best if you double-check that it's safe to do so before proceeding. Turn off all light switches and all electrical devices attached to the affected circuit before resetting the GFCI.
Please turn off the affected circuit breaker and reset the GFCI before turning it back on. Listen for a click after pressing the Test button. It signifies the ground fault interrupter has triggered if it doesn't click. Now push and hold the "Reset" button until it clicks; this should restore power to the outlet as well as all lights and outlets downstream.
The fault that caused the tripped GFCI may still exist if it doesn't reset after you've clicked the reset button. For example, suppose the GFCI continues to fail to reset, and the power has gone out throughout the house. In that case, this indicates a more serious problem that may necessitate the services of a licensed electrician.
3. Examine Your Power Sources
It is likely that one of your electrical outlets is damaged or has a loose wire. Other outlets may be losing power as a result of this problem. It's like old Christmas lights. When one stops working, it sets off a chain reaction of failures.
Your home's outlets may be wired in this manner. If that's the case, you'll most certainly require an electrician to identify which outlet generates the chain reaction and repair its wiring.
4. Examine the Fuses
Inside the fuse, look for burned glass or a broken filament. Both of these signs point to a blown fuse resulting from a short circuit. Replace your blown fuse with one of the same type and amperage.
5. Connection Error
Assume you haven't restored power to the outlet after inspecting the breakers and attempting to reset the GFCI. For example, maybe the power is out in one room, but the breaker hasn't tripped, and the electrical plug isn't working. Other outlets may be losing electricity as a result of this problem. The issue is most likely that one of your outlets is broken or has a loose wire.
You can also DIY it by removing the outlet from the box and inspecting it for any loose connections. When you remove your outlet and inspect the outlet box, you might notice one, two, or even all three of these loose connections. When one outlet stops working, look for one of three types of loose connections:
a) Loose Terminal Screws
- First, look for any loose or broken wire in the screw terminals.
- At each screw terminal, bend the wire with caution.
- It indicates that the wire is loose if it turns under the screw or if the screw moves.
- Keep an eye out for any cables or screws that are burned, damaged, or rusted.
- Replace the outlet if you discover a loose connection.
- You'll need to bend a loop to the ends of the ground, neutral, and hot wires to install the new outlet.
- Connect the hot and neutral wires with the brass and silver screw, respectively, and the ground wire to the green ground screw.
- Tighten the wires by looping them around the screws in a clockwise motion.
- Connect the pairs with a third six-inch length of wire(a pigtail) under one wire connector if the outlet you're replacing is wired with pairs of hot and neutral wires (which are under all four screws).
- Finally, attach each pigtail's loose end to its corresponding outlet screws.
b) Loose Stab-in Connections
Some electricians connect outlets by pressing stripped wires into holes on the rear of the outlet to save time. Although this wiring method does not violate the electrical code, the wires may loosen over time, producing issues. To correct this, take the following steps:
- Look for stab-in connections when troubleshooting the dead outlet.
- Gently tug each wire to check for loose connections.
- You shouldn't just put the wire back in if you find any loose connections.
- Rather, cut and strip the end of the wire before connecting it to the screw connection.
- If your wiring is aluminum rather than copper, it's preferable to leave it to a qualified professional to handle.
c) Wire Connections with Loose Wires
Here's how to tug wires at connectors to check for loose wires at wire connectors:
- Check to confirm that the main circuit breaker is switched off.
- Take hold of the wire connector.
- Carefully tug on each wire in the bundle to determine if any are free.
- Remove the wire connector if you find a loose wire.
- Cut and remove all the wires in the bundle.
- When doing so, leave 12 to 34 inches of fresh copper wire exposed.
Follow these procedures to reinstall the connector:
- To identify the correct number of wires to join, read the label on the wire connection box.
- Gather the wires and twist on a new write connection after ensuring their ends are aligned.
- Make sure it's turned clockwise.
- Re-energize the main circuit breaker.
- Check the outlets once more to check whether the issue has been resolved.
- What if the issue isn't with the wiring? The breaker may be the only thing that's broken.
6. The Breaker isn’t Working Anymore
If you've ruled out any other possible causes for the power outage, the simple truth is that the breaker is most likely broken. It is frequently the situation when your home's lights aren't working, or the problem isn't related to an outlet. The problem is resolved by changing the breaker. Call a licensed electrician if you don't know how to do it yourself.
Circuit Breaker Replacement
If your breaker trips frequently or does not trip when it should, is hot to the touch, or cannot be reset, it must be replaced. If you're not sure you can replace it on your own, consult a professional electrician. You don't want to be in a position where the electrical outlets aren't working, but the breaker isn't tripped all of the time.
If you need to replace a faulty circuit breaker that is on but not providing power to the outlet, you'll need the following items:
- Ensure that the new circuit breaker is the same brand, model, make, and size as the old one.
- Standing on an insulating surface
- Wire strippers, a separate flashlight, and a screwdriver
- Connectors for cables
- A voltage-testing device
Follow these steps to replace your circuit breaker if the outlet has stopped working, but the breaker has not tripped:
- Individually turn off the circuit breaker's branches.
- Turn off the primary circuit breaker after that.
- Test all of the cables using the voltage tester.
- Make sure the wires are completely dead before proceeding forward.
- Remove the cover from the breaker panel.
- Disconnect the load terminal from the breaker's wire.
- Remove the old circuit breaker.
- Place the new breaker in the appropriate location and gently push it in.
- Connect the load terminal to the wire.
- Replace the panel cover after tightening any loose terminals.
- Turn on the main breaker, then the branches one by one.
- Use a voltage tester to check.
However, sometimes the issue is a little more complicated. For example, you may replace the breaker only to discover that the problem persists. It usually indicates a wiring issue, in which case it's preferable to leave it to an electrician than to risk making things worse and potentially hurting yourself in the process. The sooner you call, the sooner they'll be able to resolve the issue and prevent future problems.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
1. Is it Possible for a Breaker to Fail and not Trip?
People frequently believe the breaker has tripped when it hasn't. Breakers can be turned on without tripping. They're made to withstand a large power surge before tripping or shutting down if the surge exceeds their capability.
The problem is that a breaker can take a lot of abuse from being turned on and off, so it may not always flip all the way to the off position, so you know it's turned off. If you keep it like this for a long, it won't destroy your house.
If you're concerned about your breaker remaining on when it should be off, slide your index finger over the end of the breaker to keep it in place while you turn it off and then on. It ensures that both ends are securely attached and cannot move as you switch them on and off.
Other indicators of an electrical problem in your home include lights flickering or bulbs blowing out too quickly. Still, these issues could also be caused by faulty wiring or overloaded circuits. If you observe these symptoms regularly, we recommend contacting an electrician.
2. What are the Characteristics of a Bad Breaker?
There are numerous indicators that your breaker is malfunctioning. The first indicator is that the breaker may be turned on, but no power is supplied to the circuit. A broken breaker will have a completely detached switch on each side, while a tripped breaker will have a noticeable gap between the two switches.
The breakers may create a buzzing noise or ignite when turned on. It may also emit a burnt odor if it's been on for a while. Follow the procedures below to determine if your breaker is bad:
- Use an electrical tester to check all of your breakers.
- If they're fine but still won't switch on, use an outlet tester to check the electrical outlet.
- Have an electrician come out if they still don't work after testing these things.
3. Why Does My Outlet Have Power but Nothing Works?
A tripped breaker or improper wiring might cause this. For example, let's say your breaker appears to be turned on, but the light is turned out. First, examine the breaker for any physical damage and, if necessary, replace it. If there is no physical damage, hold the breaker in place with your index finger on the end while resetting it to the off and then on positions.
If this does not solve the problem, examine your circuit box for any loose wires or other sorts of damage before consulting an electrician. If everything is in order, contact an electrician to see if your wiring needs to be fixed.
4. What Causes a Breaker to Fail to Reset?
Circuit breakers are made to be quickly reset. However, there are a few reasons why a breaker might not reset.
- The breaker is already turned off, and the switch is turned on.
- A tripped circuit breaker.
- The breaker isn't working because there isn't any power.
- There isn't a connection between the grounding wire and the circuit breaker.
- A fuse may have blown.
- The wires are in contact.
5. How Does a Blown Breaker Appear?
Tripped circuit breakers cause the outlets to lose power. A blown breaker is usually caused by a problem with the wiring or a problem with the fuse box in your home. If you turn the breaker on and off a few times, it will usually function again.
6. What is the Procedure for Inspecting a Circuit Breaker?
The majority of circuit breakers have a straightforward design. There will be a toggle switch on one side, and on the other, there will be a button. It makes it simple to distinguish between the two breaker positions. If you're unsure, check the breaker's label or markings to see which position is "on" and which is "off."
If you can't find them, you can check your electric panel by turning each breaker on and off to determine the correct position. Flip the lever over and push it into place with your index finger once you've determined which one is "off." The circuit breaker should be turned off.