Energy performance was probably not on the list of reasons why you picked those last window sets— was it? Don’t worry, you and me both 😉 So here we are; you’ve finally caught on to the energy-saving window concept wave— welcome to the club! If you are planning to install energy-efficient windows in your home, you are likely wondering; what style of window is most energy-efficient?
As a homeowner, I set out on a quest to best answer this question for my home renovation. From plenty of research and trials, I was able to round up a few of the best energy-saving window options. Here’s what I found out.
Are Energy-Efficient Windows Worth All the Hype?
We can all agree that windows are one of the best ways to let the outdoors seep into our indoor space harmoniously. So obviously, we all want to capture the best and most beautiful view possible. But, besides breathtaking views, windows with energy-saving features can also noticeably lower your home’s energy costs.
Optimum energy efficiency, in the form of thermal performance, is determined by factors such as the type of glass, frame features, overall quality of the window, and others. Even then, the window should be installed properly by experts for peak efficiency.
Besides significantly lowering your energy cost, here are more reasons why you’ll want to pick new windows with energy-saving features.
Benefits of Energy-Efficient Windows
Energy-efficient windows are wildly gaining popularity now because they have several advantages over standard options.
i) Increased Insulation
Increasing your home insulation is one way to boost your energy efficiency. For example, energy-efficient windows have more insulating features to provide better protection from outside temperatures. In addition, some of these windows come with voids that you can fill with insulating materials for extra shielding.
Most energy-efficient windows tend to have layered glass. For instance, a double-pane window, also known as a dual-pane window, comes with two layers of glass with space in between. In addition, there have insulative gas fills (most likely Argon or Krypton gas) sandwiched between the layers.
Further on the list, we have triple-pane windows consisting of three layers of glass panes and two compartments filled with insulative gas. An extra layer of glass translates to lower air leakage rates which equate to a lower heat transfer rate and higher thermal protection inside the house. After all, increased energy efficiency also means that your heating and cooling systems aren’t working as hard to keep the temperatures in the house optimum.
ii) Better Noise Reduction
Another benefit I was elated to stumble upon is the improved noise reduction. Interestingly, from my research, sound mechanisms also operate on similar energy-efficiency rules as thermal performance.
This means that, as a homeowner, every layer of insulating glass you add to the windows means an extra layer of soundproof protection from any outdoor noises. So we finally have a solution to road noise, noisy lawnmowers, and so much more— especially on mornings when you are trying to sleep in and want nothing to do with the world outside.
In essence, this also means that energy-efficient windows with two or three layers of glass will keep your home quieter compared to windows with just one layer.
iii) Decreased Condensation Rates
We can all relate to this one— the condensation nuisance that causes damage to window wood frames, floors, furniture, and other wooden items. This happens when one side of the glass pane has a lower or higher temperature than the other. The moisture within the air on the warmer side condenses once it touches, the cooler side of the glass.
Not only does this make your windows foggy, obstructing your view of the outside, but it also creates a dump atmosphere that damages window frames and any wooden items nearby.
Like the rest of the perks with energy-efficient windows, a triple-pane window will likely experience less condensation than a single-pane window.
What Factors To Consider When Choosing the Most Energy-Efficient Windows?
This is the trickiest part in the purchasing process— but worry not, I did my homework so you wouldn’t have to.

Image Credit: pinterest.com
Tip: Window ratings and labels are a great place to start when you need basic information to compare different products. However, certain window features will affect your home’s energy efficiency that cannot be easily explained using a sticker.
Here are some factors you will need to consider to find the most ideal energy-efficient windows for your home:
A. Window Types that Increase Your Home’s Energy Efficiency
There are many window styles popular with architects in the market, and each is suited for different purposes and temperature conditions. In addition, different window panes contain at least one, if not all, design features that help increase energy efficiency. Here are some window types you should consider and a quick rundown of the reasons why they are the best options in the market:
1. Completely Fixed Windows
Completely fixed windows, otherwise known as picture windows, are one of the most energy-efficient window types since they are completely sealed to the window frame. They have such an impeccable energy-efficiency level since they come with non-operable sashes and no seams.

Image Credit: pinterest.com
Completely sealed specialty or picture windows don’t allow conditioned air to go out; since there are no moving parts, virtually no air can penetrate through. This is actually a good thing when it comes to energy efficiency in a sunny climate. After all, the airtight seal on a picture window makes it one of the most energy-efficient window styles.
Of course, this comes at the cost of being able to open and close these window panes for fresh air. For this reason, it’s best to pair them with functional window units for natural ventilation when needed.
Fixed picture windows are best for parts of the home that don’t need ventilation. They also work great in wall window designs, where the airtight design will help keep areas with large expanses of glass from feeling a little drafty.
2. Casement or Awning Windows
If you need functional windows, hinged casement or awning windows rank high as one of the most energy-efficient windows right after fixed windows. Why? Since they also create a firm weathertight seal when closed.

Image Credit: pinterest.com
The singular sash on casement windows presses firmly against its frame when closed, which keeps air movement to a minimum for energy efficiency. Casement windows that lock at multiple points are more airtight and therefore have high energy efficiency.
3. Bay and Bow Windows
Another window type that delivers excellent energy efficiency is the bay and bow window, especially when it includes the casement window design.

Image Credit: pinterest.com
Even with no fixed panels, a bay window will offer more energy efficiency since it has fewer openings and less air infiltration.
4. Double-Hung and Sliding Windows
If you prefer installing operable windows, sliding and double-hung windows are also great options. They are two of the most popular functional energy-efficient window designs.
As the name suggests, sliding windows are designed to move horizontally along a track. They tend to be larger than most single or double-hung windows, and some slide windows have options to open from either side.
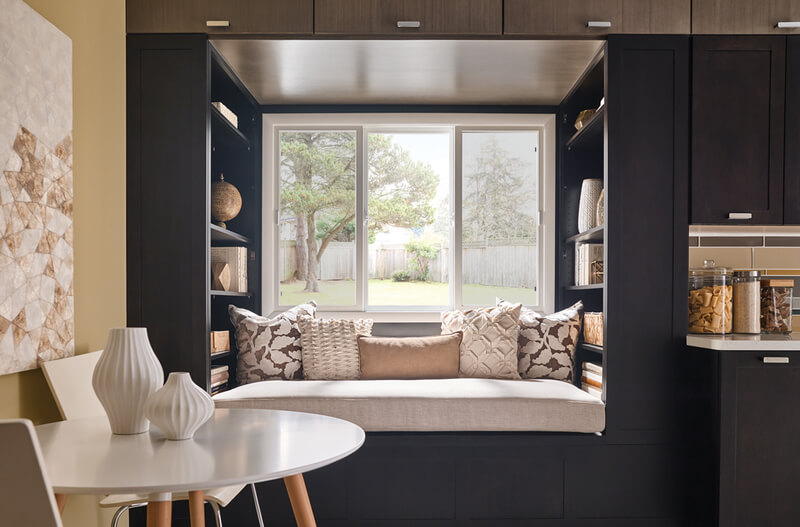

Image Credit: pinterest.com
These windows have slim vertical lines, which give the window a clean and elegant profile. Additionally, their profile also offers the room maximum visibility of the outside.
Tip: Sliding windows are generally more energy-efficient than double-hung windows since they have fewer moving parts and interlocking panels. These features reduce the chances of air leakage.
On the other hand, double-hung window designs come with two sash windows within a single frame that can be easily retracted or extended for ventilation or thermal performance.
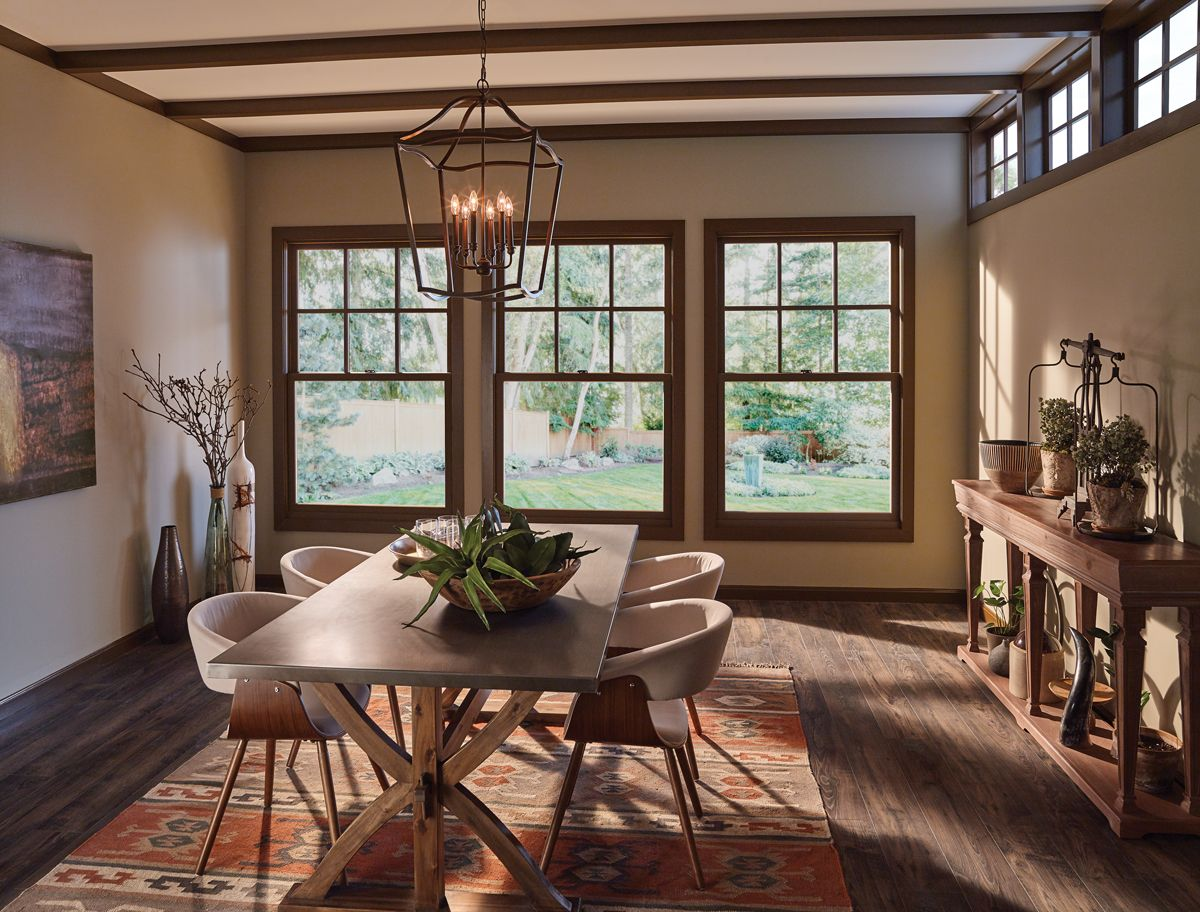

Image Credit: pinterest.com
Modern designs have greatly advanced air leakage prevention and design improvements. For instance, they now have staggered sashes that reduce air movement when closed.
Tip: Double-hung window designs are best used in spaces where the room’s height is much greater than the width. They also work well with bay windows in the corners of the room.
These are the perfect new windows for anyone who’s aiming for a ‘flooding light’ look.
5. Hinged Windows
Hinged windows are specifically designed for increased ventilation, besides energy efficiency. They are characterized by a pivot hinge that twists or can be pushed outward.
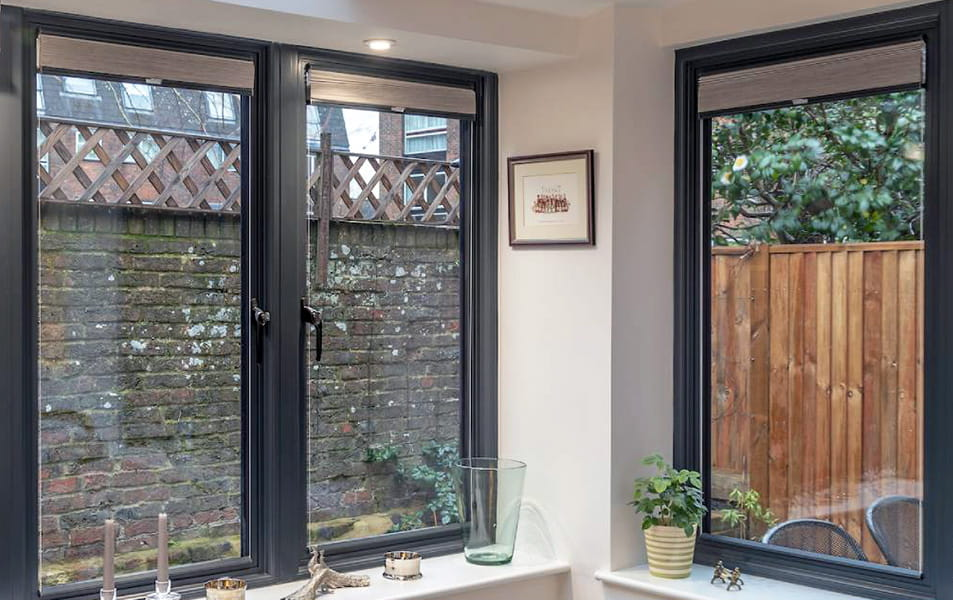

Image Credit: pinterest.com
The hinge design firmly presses against the frame for less air infiltration. This design is more energy efficient than double and single-hung windows, which have window sashes overlapping each other.
Tip: Hinged windows can be used for strategic ventilation since they pair perfectly with airtight sealed windows.
Awning, casement, and hopper windows all fall under hinged windows. The only difference among the three is where the hinge is positioned; at the top, side, or bottom, respectively.
6. ENERGY STAR® Windows
The National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC) label is one way to check the energy performance ratings on most energy-efficient windows. To help you identify windows that have undergone testing and are approved, check for the blue ENERGY STAR sticker.

Image Credit: pinterest.com
ENERGY STAR® windows are certified to have lower air leakage rates. So windows with an ENERGY STAR® logo most likely have a higher energy efficiency than one without.
Note: ENERGY STAR® ratings are based on the climate and geography of a specific location. This means that a highly rated window in the sunny Southwest may not perform as well in the windy Northeast.
These energy ratings by ENERGY STAR® make purchasing windows most suitable for your home easier.
7. Insulated Windows
Adding an extra layer of glass is one way to provide extra insulation. According to the NFRC energy efficiency, this lowers the Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SGHC) and U-Factor for a higher window energy efficiency.

Image Credit: pinterest.com
Today, insulated windows don’t just have an extra layer of glass; insulating gas also fills each layer separately. For this reason, triple-pane windows actually offer a higher energy efficiency rate than single-pane windows.
8. Low-E Windows
Besides the window style, whatever is outside the window pane also matters.
A lower emissivity coating, also described as a Low-E coating, on window panes makes up what is often described as a Low-E glass window.

Image Credit: pinterest.com
The low E-coating on a Low-E glass window is designed to block ultraviolet (UV) and infrared rays but let in visible light. This helps to boost its thermal performance.
Infrared light affects heat energy, so by blocking it out, Low-E windows help keep the sun’s heat energy from entering the house.
Tip: These window designs are perfect for homes in predominantly hot places. Plus, it has higher energy performance ratings compared to the other builds.
Interestingly, Low-E glass windows also efficiently work oppositely in places with colder climates. How? They can actually reflect heat into the house to reduce heat loss and maintain thermal efficiency.
Tip: In colder climates, double-pane windows with low E- coatings work better in thermal performance than triple-pane windows with low E- coatings.
B. Type of Window Frame Material
There are many window frame materials on the market ranging from vinyl to metal, wood, fiberglass, and so much more.
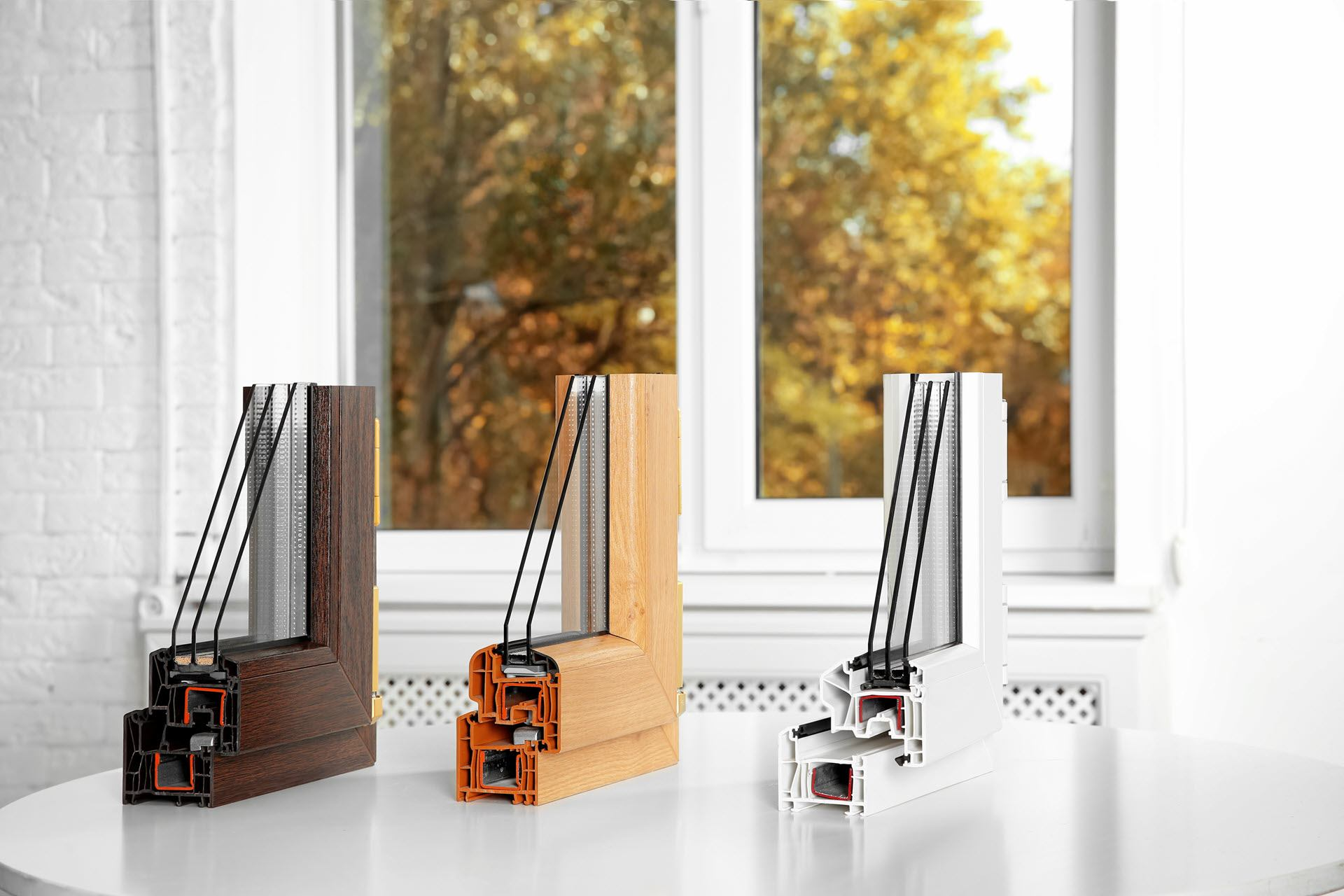

Image Credit: pinterest.com
1. Vinyl
Of all mentioned, vinyl ranks as the most energy-efficient frame material since it has better natural insulating properties than fiberglass and metal. This means that it won’t warp or deteriorate like wood frames often do with time.
I also found out from my research that vinyl has a higher R-value. This means that it effectively reduces heat transfer in and out of the house, keeping warm air inside during winter and outside during the summer.
The only downside is that they’re slightly pricier and cannot be painted.
2. Aluminum
Aluminum frames are the most affordable but also the least energy-efficient. Fortunately, they require minimum maintenance and can be painted according to your preference.
3. Wood
Wood frames are slightly less energy-efficient than insulated vinyl but more energy-efficient than aluminum. They’re also pricier than vinyl window frames, but most homeowners prefer them for their aesthetic appeal and durability.
4. Composite
Composite frames are made from different materials to offer the appearance of wood frames but with much superior energy efficiency. For this reason, they are more expensive than vinyl, aluminum, and wood frames.
5. Fiberglass
Out of all these, fiberglass is the most durable and priciest window frame material. It is also one of the most energy-efficient materials.
C. Brand Reputation
Name brands aren’t always everything, but when it comes to energy-efficient windows, brand reputation gives you a sense of the quality.

Image Credit: pinterest.com
For instance, Vinyl may have great natural insulating properties, but a poorly manufactured vinyl window frame won’t provide as high energy efficiency as a great quality wood frame.
Frequently Asked Questions on the Most Energy-efficient Windows
1. Which windows have the highest heat loss rate?
Single-glazed windows with clear glass have the highest energy transfer, which translates to a high heat loss or gain depending on the local climate. They also allow the highest sunlight transmission, which is why they are practically extinct in residential architecture.
2. What else should I consider when buying energy-efficient windows?
Besides what we have discussed, check for a low SHGC. The SHGC unit measures the amount of solar radiation that passes through a window. A low SHGC means reduced heat loss and gain in different climates. A low U-Factor also helps you maximize energy savings in different climates.
3. Which energy-saving windows provide the best airflow?
Casement windows are your best bet for maximum ventilation since they consist of one sash window that can be cranked open to direct and control drafts effectively.