Before committing to solar, every consumer must consider whether the switch is worth it. This typically comes from knowing how much energy your roof-installed panels can produce. Also, you’d like to determine if the energy generated will be enough for your household needs. In any case, several factors will influence a solar panel’s energy production capabilities. But how much energy do solar panels produce?
With the significant drop in the cost of solar, it is realistic for homeowners and business owners to leverage the power supply. A typical home needs around 10,000kWh per year, which 20 to 30 panels can generate. But just as every home is different, so are solar panel systems. Besides, their production is also determined by various factors that we will discuss later.
In this article, we explore how solar panels work to generate power and how to calculate the amount of energy they produce. Dig in!
How Do Solar Panels Work?
Simply put, solar power is created when particles of light, photons, hit the photovoltaic(PV) cells that make up your solar panel system. These solar cells convert the electrons into electricity when photons are absorbed by the PV cells.
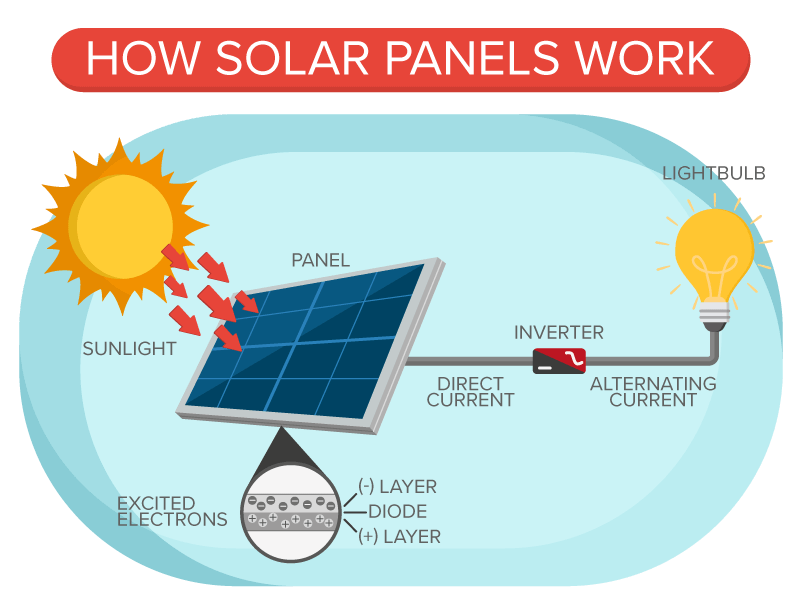
Image Credits: medium.com
Solar panels are made up of thousands of photovoltaic cells. These cells create electrical charges and cause electricity to flow.
Solar panels offer several perks, including reduced bills, a renewable energy source, environmental benefits, insurance against rising energy costs, and energy independence.
Key Solar Panels Terms
i) Kilowatt (kW)
This is a measuring unit of electrical energy equaling 1,000 watts. The electricity generated by a solar panel can be expressed as watts or kilowatts.
ii) Kilowatt-hour (kWh)
This is a measure of electrical power equal to the consumption of 1,000 watts per hour. Kilowatt-hour is used as a billing unit for the energy an individual consumes. Additionally, 1kWh equates to 3.6 megajoules.
iii) Direct Current (DC) Power
This is power initially generated from the solar panel.
iv) Alternating Current (AC) power
This is the power used by household appliances. The DC power generated gets converted into AC so consumers can use it in their homes.
How Many Watts Does a Solar Panel Produce?
The energy produced by a solar panel, also called wattage, depends on several factors, including panel efficiency and peak sunlight hours, and is measured by kilowatt-hours. Most residential solar panels generate around 250 – 400 watts, but panels for larger homes can produce 750 – 850 per kilowatt hour annually.

Image Credits: abgross.co.za
Solar panel manufacturers determine the solar energy output based on zero obstructions. But, the solar power a panel produces depends on its energy output and the number of peak sunshine hours in the system’s location. Therefore, the information from the manufacturer should be a starting point for calculating your needs.
How to Calculate How Much Power Solar Panels Produce
The solar panel wattage describes the peak quantity of power it can generate. Assuming no obstructions, manufacturers generally test performance at 77 degrees Fahrenheit. But because real-life conditions are complex, solar panels’ output is anticipated to be lower than the manufacturer’s maximum rating.

Image Credits: nairametrics.com
With the wattage rates of a solar panel, you can determine how much electricity your solar panel produces using this simple formula:
Watts x Average peak sunlight hours= Kilowatt-hours/1000
For example, if a 400W solar panel receives five hours of sunlight daily, the total power output is calculated by multiplying 400W x 5h = 2000Wh/1000 or 2.0 kWh.
This approach makes it easy to calculate energy production by week, month, and year. For instance, in a year, your solar panel would produce;
(2.0kWh/day) x (365 days/year) = 730kWh per year
It may be unclear how many peak sunlight hours to expect. However, several solar installation companies produce tables of estimated exposure within the installation service zone. As a result, a solar panel can produce more or less than advertised depending on the roof angle and prevalent weather conditions.
What Impacts the Amount of Energy Solar Panels Produce?
Four main factors determine how much electricity your solar panels produce. These are as follows:
1. The Solar Panel Size
This is the most important factor that affects the amount of solar energy your solar panel produces. The larger the system is, the more solar cells there are for electricity production. A typical installation produces 3.5kw, and this takes around 12 panels. Alternatively, the 1kw domestic system takes only two to three panels. Solar panels normally have either 60 or 72 solar cells, and obviously, 72 solar cells have higher electricity production.
2. Direction
The direction your roof faces and its angles are other important factors affecting solar energy production. For optimum performance levels and efficiency, the positioning of the panels should be facing south to capture the maximum amount of sunlight. Solar panels installed facing southwest, southeast, north, east, and west will have a typical output loss of 8% to 30%.

Image Credits: gienergy.com.au
Also, the south-facing panels should be tilted between 30- and 40-degree angles to ensure sunlight hits panels at a perpendicular angle, which produces the most energy. The angle of inclination of the solar panels should be adjusted according to variations in seasons, latitude, longitude, and sunshine hours.
The roof area where the solar panels are installed should not be in the shade during the day. Allowing the solar panels to be under the sunlight all day increases the amount of electricity your panels produce.
3. Seasons
The time of year has an impact on panel efficiency and energy production. During the summertime, daylight hours are longer, so energy production is higher. However, it is important to note that solar panels work by capturing light as opposed to heat, and they will produce energy throughout the year.
4. Solar Panel Efficiency
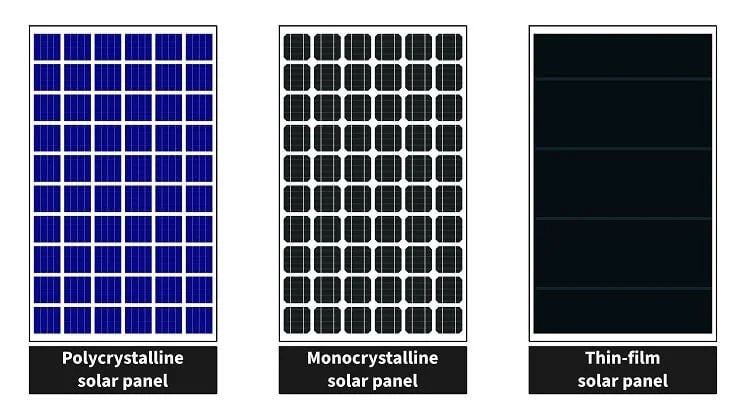
Image Credits: greenhomemakeover.com
Hundreds of solar panel models are on the market, all with unique efficiency ratings, wattages, and degradation rates. Solar panel efficiency impacts solar power production. While there is a lot to consider, deciding on the panel to buy is a good place to start. For instance, monocrystalline and polycrystalline are two different types of solar panels with different capabilities. Some of the features of each technology include;
a) Monocrystalline Solar Panels
- More expensive
- Higher efficiency
- Better performance in shady conditions and high temperatures
B) Polycrystalline Solar Panels
- Less expensive
- Lower efficiency
- Less efficient at higher temperatures
Despite the different levels of efficiency, these two solar panels offer more efficiency because the electrons that generate electricity can move. Manufacturers use pure and melted silicon crystals that make electrons move freely. Polycrystalline cells have an efficiency rate of 12 to 16%, while Monocrystalline cells have an efficiency rate of 15 to 20%.
How Many Solar Panels Do You Need for Your Home?
To determine how many solar panels can power your household requirements, you can multiply your hourly energy requirement by peak sunshine hours and divide the outcome by a panel’s wattage.

Image Credits: pinterest.com
For instance, using a low wattage of 150 W and a high wattage of 370 W, you can establish a range of 17-42 panels to generate 11,000 kWh/year. Keep in mind that the size of your roof and how much sunlight your roof gets are also factors that determine the number of panels you need for your solar panel output demands.
Also, your energy demands will determine the number of solar panels you install. For instance, more complex activities like charging electric cars will require 5 to 10 solar panels.
What to Do With Excess Electricity Produced
This is a good problem to have. Excess solar energy production happens if you modify your energy use if you have more panels than is necessary and during prolonged peak sunlight hours. In these cases, surplus energy is produced, and your energy utility provider might give credit if you return the excess power to the local grid.

Image Credits: thesolarpeople.co.uk
Excess solar energy generates net metering credits that can help you establish self-reliant energy, meaning you will not rely on the local power grid. A backup solar battery is more realistic than installing an in-house energy storage system. But, depending on your home size and energy consumption, both methods could be suitable.
Checking the Efficiency of the Solar Panels
The simplest way of checking if your solar panel is efficiently working is by checking the inverter. Check the color of the lights on the box during the day when the system is meant to be running.
A green light on the inverter means the system is functioning properly, while a red or orange light during daylight hours means there is a system fault.
When there is a red or orange flashing light, look for an error code on display. Alternatively, you can go to the inverter’s user interface online for an indication of the cause.
If there’s an error message, call the installer. Do not tamper with the system to avoid risks such as solar panel fires.
Inverters can break down due to a grid fault where the voltage is too high or too low and when there is a problem with the system’s earthing. Also, the circuit breaker may trip, causing an inverter to break down.
You can also check if the solar panel produces as much power as it should by comparing the actual output with the estimated amounts in the owner’s manual. If you’re worried that your solar panels are underperforming, contact the installer or manufacturer. They can send out a solar panel expert to investigate.
Bottom Line
All solar panels may look similar, but they are not created equally. Different models produce varying amounts of energy. With this information, you can choose the type and number of solar panels for your savings and off-grid living.
Proper installation and maintenance significantly affect the efficiency of your entire solar panel system. So, with an array of solar panels on your rooftop and optimal efficiency, be sure of self-reliant energy and much savings.
Featured Image Credits: build-review.com