A Fabric Revolution: The Basics of Fabric Buildings
Fabric structures, tension fabric structures, or tensile structures are distinct from conventional construction materials and techniques. They include a load-bearing structure usually in the form of steel cladding or aluminum, and a tensile fabric. This material, usually PVC-coated polyester or PTFE-coated fiberglass, is tensioned across the frame to form a sleek and effective structure.
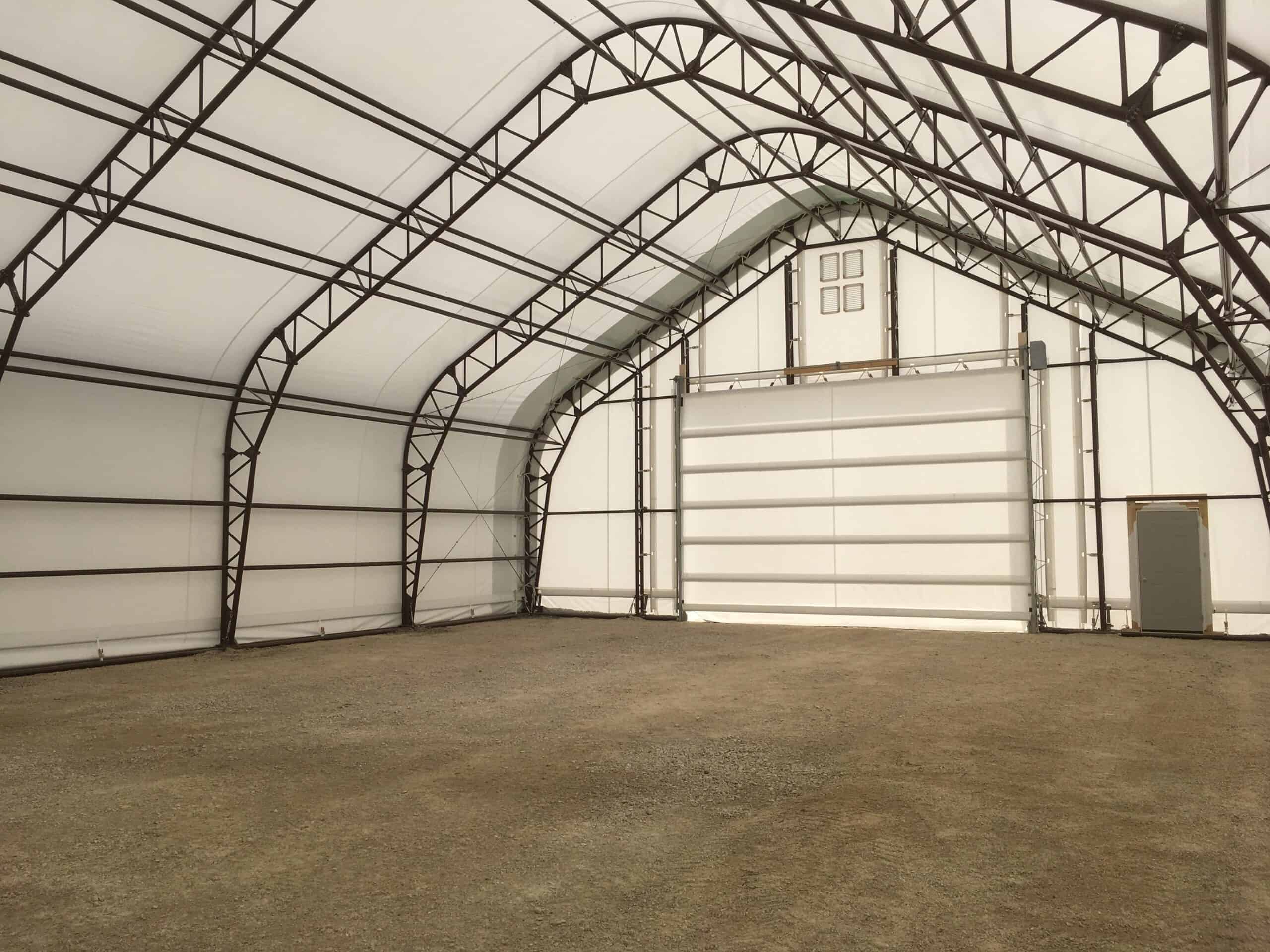

Image Credits:fastcoverbuildings.com
The nature of fabric structure makes these them highly versatile. This makes it possible for large clearspan fabric structures to be created because few internal supporting columns are necessary. Also, the fabric is translucent and allows sufficient natural light to penetrate the building, thus eliminating artificial lighting during the day.
Types of Fabric Buildings
1. Tensile Structures
Tensile structures are recognized by employing the tensioned fabric membrane spanning between lightweight support structure. Due to the tensile nature of the fabric it is capable of withstanding certain environmental loads like wind and snow loads. These structures can be of any shapes, ranging from mere curved designs to designs such as the hyperbolic paraboloids. Tensile structures are commonly incorporated into architectural designs for its aesthetic value and versatile forms.
2. Air-Supported Structures
Air-beam structures depend on a vacuum or pressure being created to support the structure’s form. It is mostly made up of PVC or ETFE (ethylene tetrafluoroethylene) fabric membrane and has numerous benefits and drawbacks.
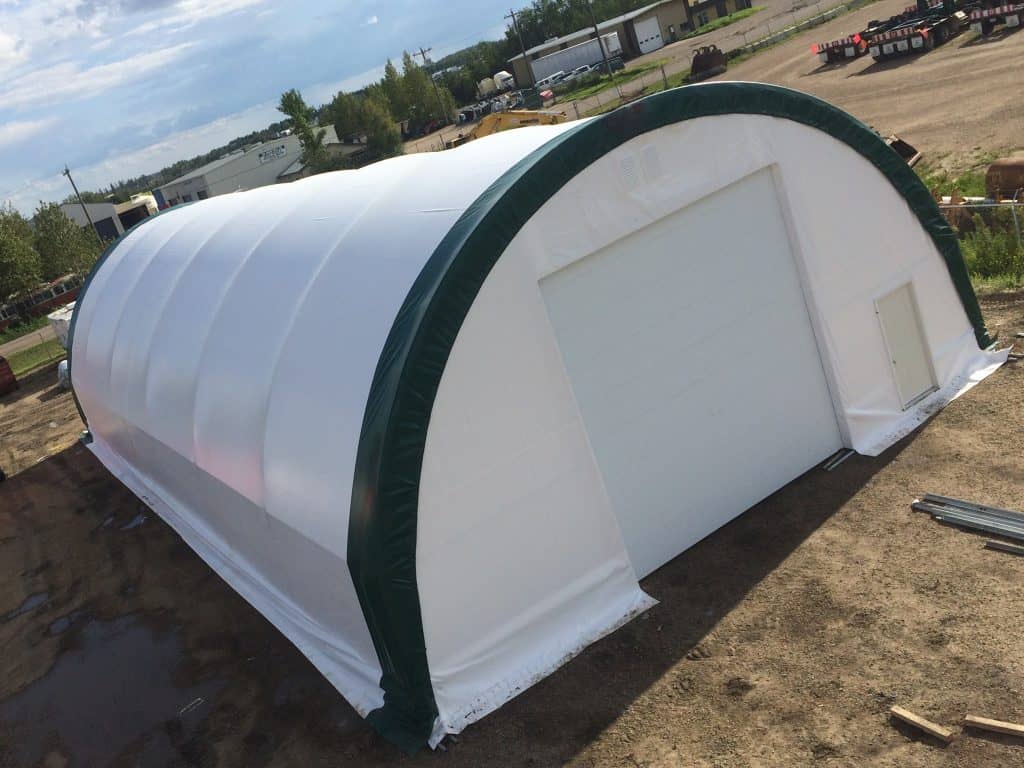

Image Credits: energynow.ca
These structures can be easily inflated and deflated, which makes them ideal for transient or relocatable situations. They have large uninterrupted ceiling spans and are applied in the construction of sports complexes, exhibition centers, and temporary shelters.
3. Frame-Membrane Structures
The frame-membrane structures consist of rigid steel or aluminum frame on which a fabric membrane is stretched. The frame is mainly for the support of the structure and the shape of the building while the fabric offers the protection from the weather and the natural light. These buildings can vary in size and form and their uses can range from industrial storage, from workshops to manufacturing plants.
4. Cable-Net Structures
Cable-net structures rely upon a system of tensioned cables for the support of the fabric membrane. The cable grid spreads the loads evenly and also provides the feeling of an open and vast interior. It is widely applied in construction of large-span buildings such as sports stadiums, convention and exhibition centers, and terminals of airports. Thus, the architectural form created can be dramatic and instantly recognizable.
5. Pneumatic Structures
These structures utilize the pressure of air within separate compartments to achieve a segmental look. These structures are also very light, can be easily transported, and are not very time-consuming to put up. They are intended for short-term uses such as in disaster relief, as emergency shelters and other novel structures where the inflatable look is appropriate.
6. Sail Structures
Sail structures copies the elegant curves of sails of a ship. The fabric is stretched between the masts or poles to form an aesthetically pleasing and a practical shading system. Sail structures are widely used in outside areas such as plazas, courtyards, and theaters and serve both a shading function as well as an aesthetic one.
7. Modular Fabric Buildings
Modular fabric buildings are made up of specifically designed modules that can be easily installed.
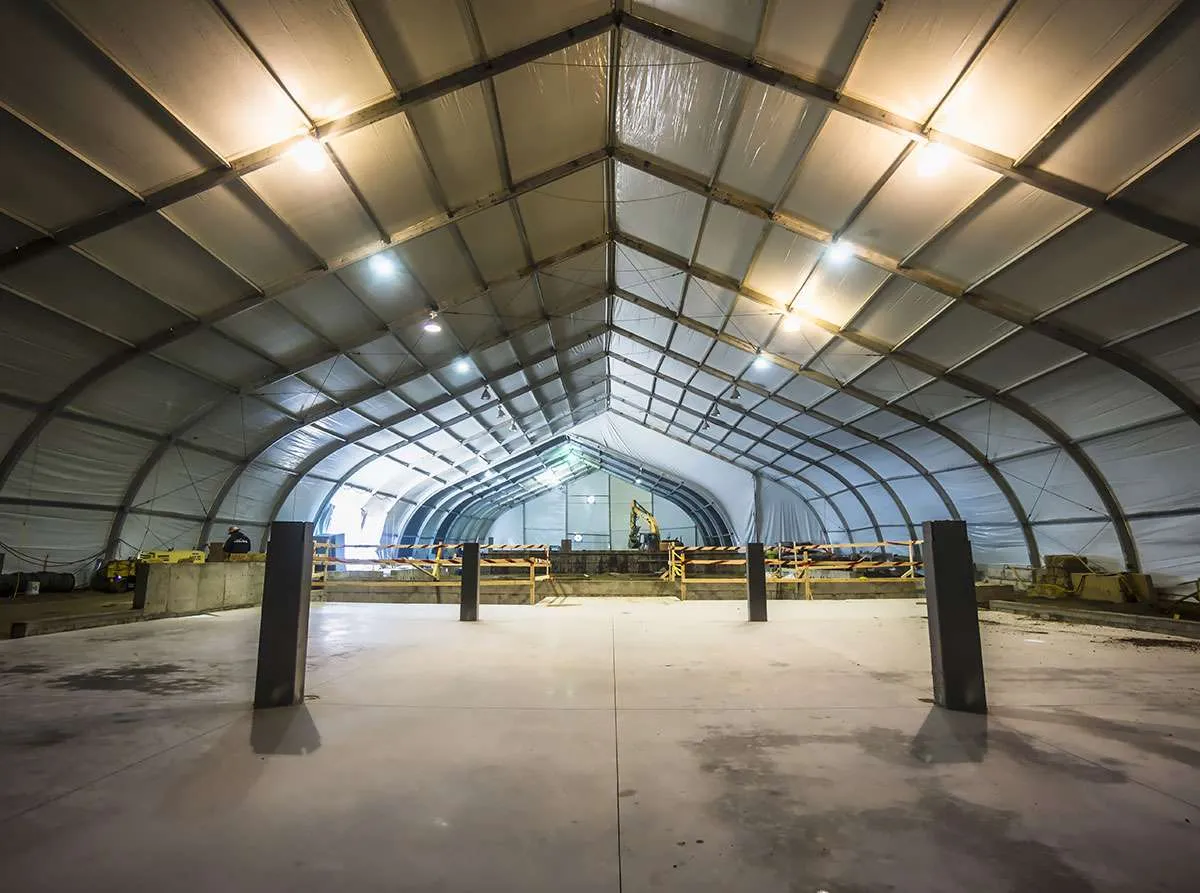

Image Credits: allsitestructures.com
These structures are therefore portable and can be expanded or moved to other places if the need arises. They are well known for use in temporary storage, construction sites, and as working spaces since they are cheaper and easily customizable.
Features of Fabric Buildings
1. Material and Design
Generally, fabric structure buildings use tough and flexible materials such as PVC, polyester, or PTFE to hold up the fabric. The material is covered on a steel or an aluminum framework. The design can be manually adjusted in terms of size, color, and other options to meet certain requirements.
2. Lightweight Construction
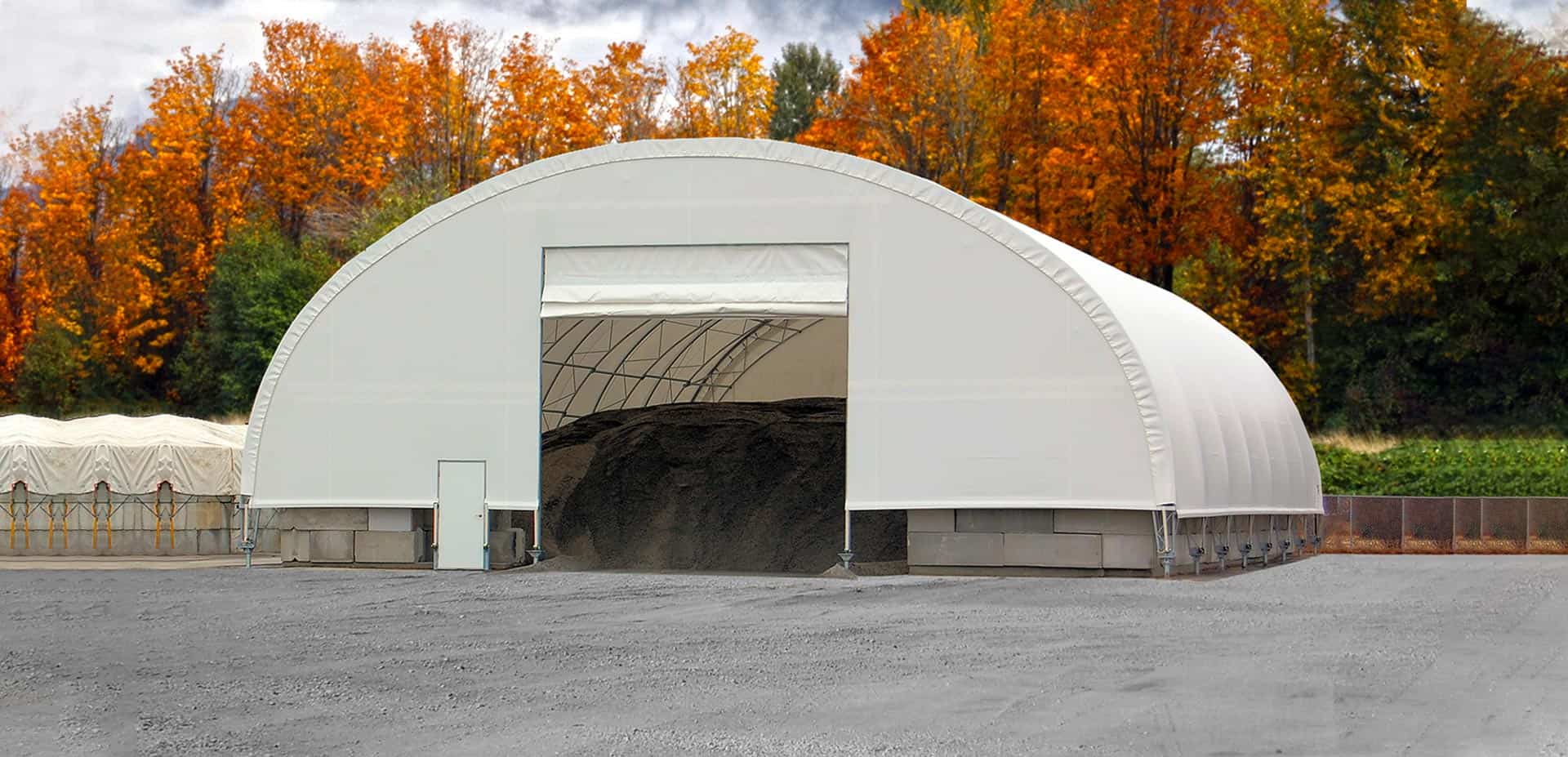

Image Credits: asicoverbuildings.com
Another unique characteristic of fabric buildings is their relatively small mass. Due to its light weight, the material can be easily transported and constructed thus suitable for use in temporary structures.
3. Translucency
Depending on the fabric utilized, these structures can provide different levels of opacity, and therefore let in natural light. It saves costs on energy and enhances the appearance of interior environment within the building.
Sustainable Materials Used in Fabric Buildings Construction
Sustainable materials do not harm the environment, they are not toxic, and require lesser energy to be processed. Here's a look at some of these materials use in a fabric building project:
1. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Tensile structures are usually made with PVC fabrics. While PVC has been an issue for the environment, most companies today have incorporated environmentally friendly PVC by using right methods and additives.

Image Credits:theconstructor.org
2. Polyethylene (PE)
This material is recyclable and can be used in fabric building construction of strong and weather resistant buildings.
3. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
PTFE is an extremely durable material that is widely used for a range of applications and is recyclable. Its inertness and its tolerance to corrosion by any given environment make it desirable.
4. Ethylene Tetrafluoroethylene (ETFE)
ETFE is a light translucent material that can be used instead of glass. It is recyclable and is a good insulator which will help cut down costs on energy.
5. Recycled Fabrics
Some fabric buildings contain recycled fibers, which helps control waste and preserve the earth’s resources. This may include fabrics developed from used plastics or any other material.
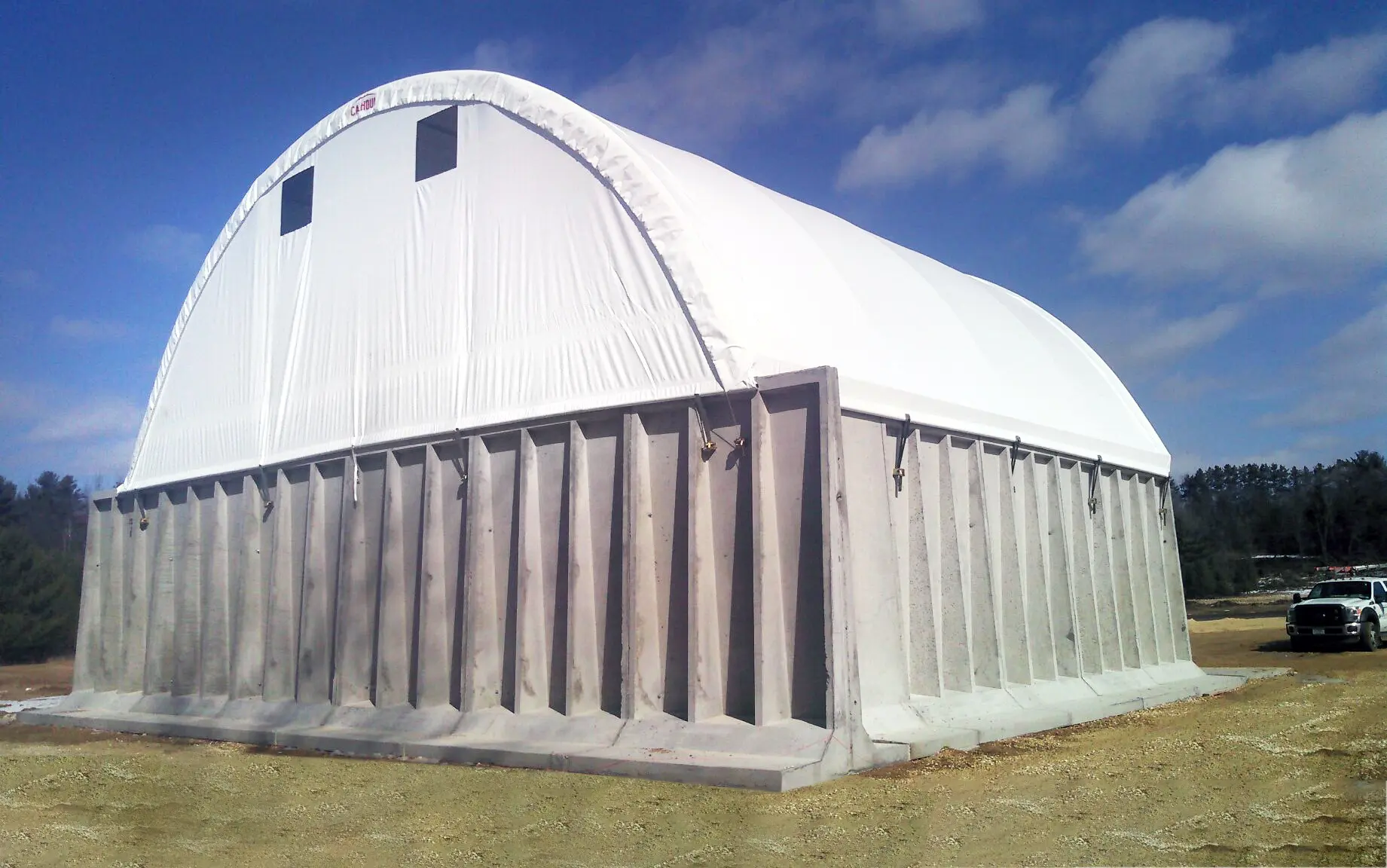

Image Credits: calhounsuperstructure.com
6. Natural Fabrics
However, materials such as hemp or bamboo, which are derived from natural sources, can also be used in the construction of fabric buildings and go a long way towards diminishing the amount of carbon emissions in the environment.
7. Coatings and Treatments
Some of the fabrics applied on tensile structures are treated with non-toxic chemicals in order to make them more resistant to weather conditions. These coatings can increase the lifespan of the material, therefore cutting down on the frequency of replacement.
8. Solar Integration
Even though solar panels are not a material, their incorporation in the fabric of the building can enhance energy usage and contribute to sustainability.
9. Efficient Framing Materials
Such frames include metal frames used in fabric buildings which are either recycled or sourced from other recyclable structures such as steel or aluminum. It has been established that their production and utilization can be more energy conserving compared to other building materials.
Innovative Uses of Fabric Buildings
Fabric buildings have a wide range of applications across different sectors, including:
- Indoor Agricultural Facilities: Agricultural Fabrics buildings and structures are suitable for year round cultivation because the fabric creates a suitable environment. This has made it possible to integrate other systems such as hydroponic systems, vertical racks and automated irrigation systems on the equipment. The used fabric is transparent allowing natural light into the rooms while at the same time controlling temperatures and humidity which is ideal for plant growth and energy conservation.
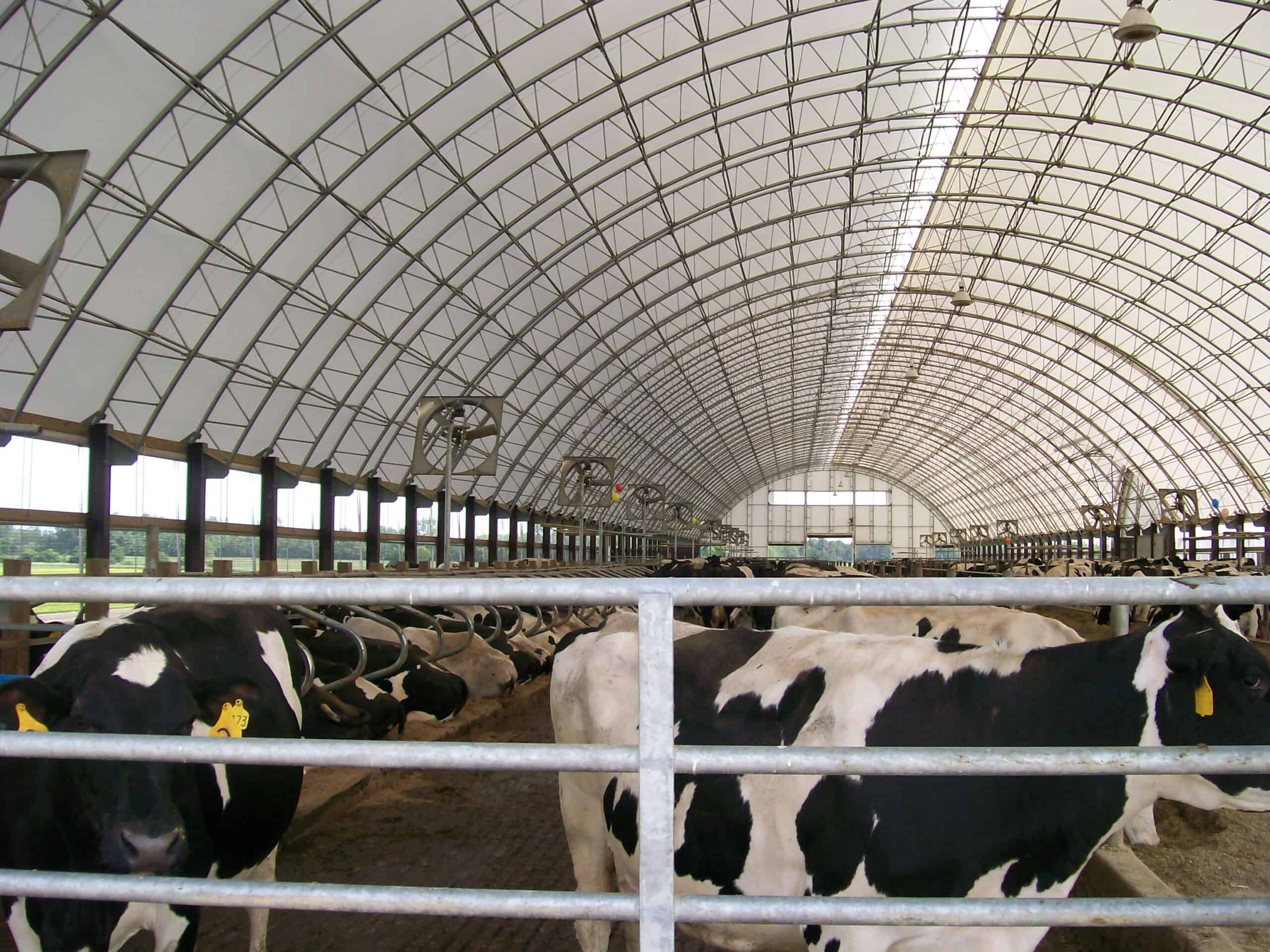

Image Credits: winklerstructures.com
- Sports Facilities: An overview of fabric structures will reveal that they are relatively inexpensive and can be used to provide shelter for indoor sports facilities or practice fields. It has a large unobstructed area that can be used to host different sporting activities, and the fabric can be arranged in a way that is appropriate for the inflow of light and air. These structures are more appropriate of holding sporting activities or even coaching sessions.
- Emergency Shelters: Such constructions can be easily installed in disaster areas and these types of structures offer a lot of versatility when used as shelters. They can be easily transported and erected thus providing shelter for the affected persons as tougher structures are being constructed.
- Aircraft Hangars: Traditional aircraft hangars are quite expensive to construct, and that is why fabric buildings can be used as an affordable solution. They can be expanded or relocated rapidly due to the modularity of their construction; therefore, suitable for private jet owners, flying clubs, or military usage in the wilderness.
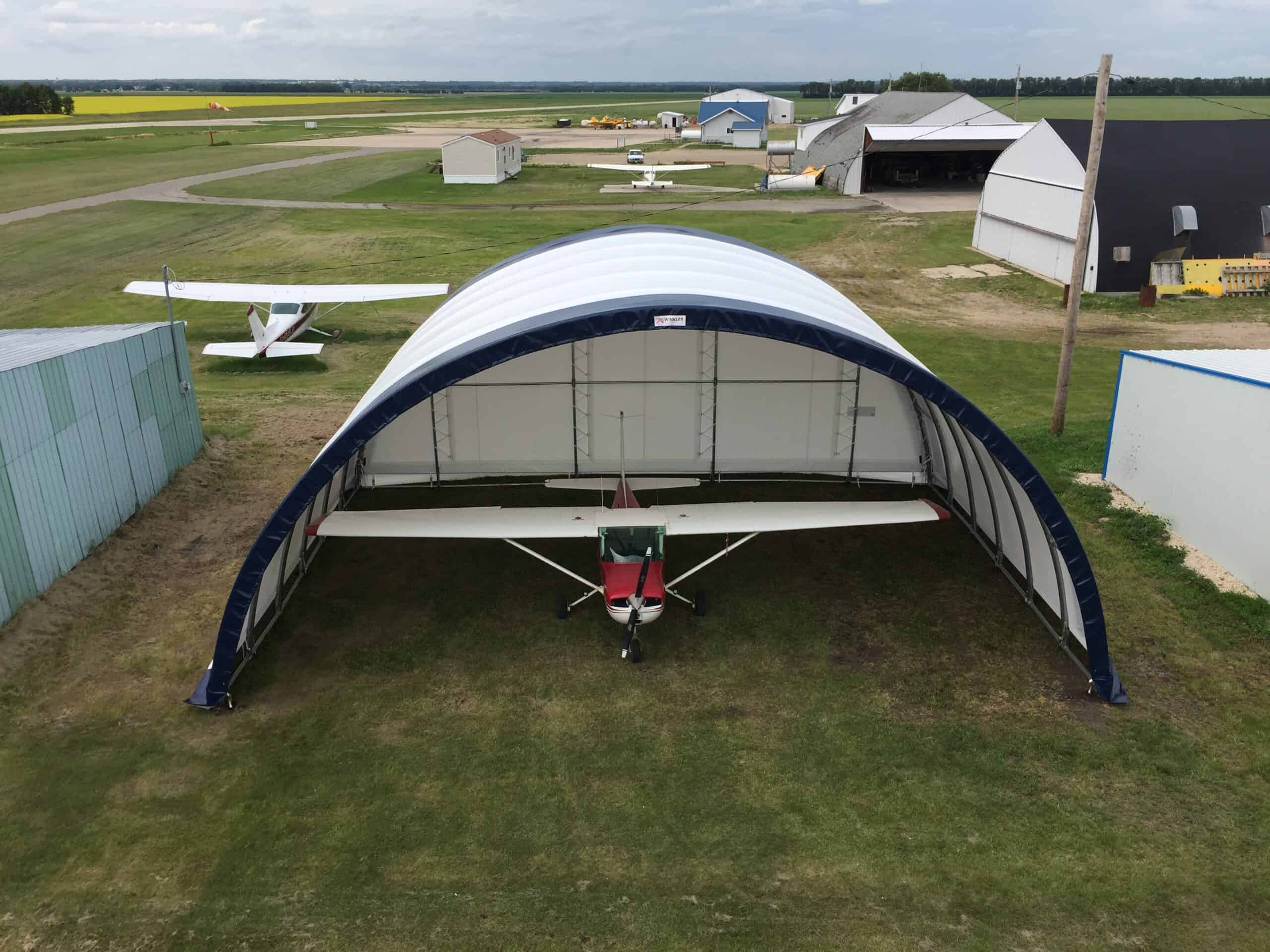

Image Credits: winklerstructures.com
- Warehouse Extensions: Fabric buildings can be easily erected in a short time especially during peak seasons or situations that call for an increase in the warehousing capacity. This flexibility allows companies to address short-term storage requirements without having to undertake long-term expansion.
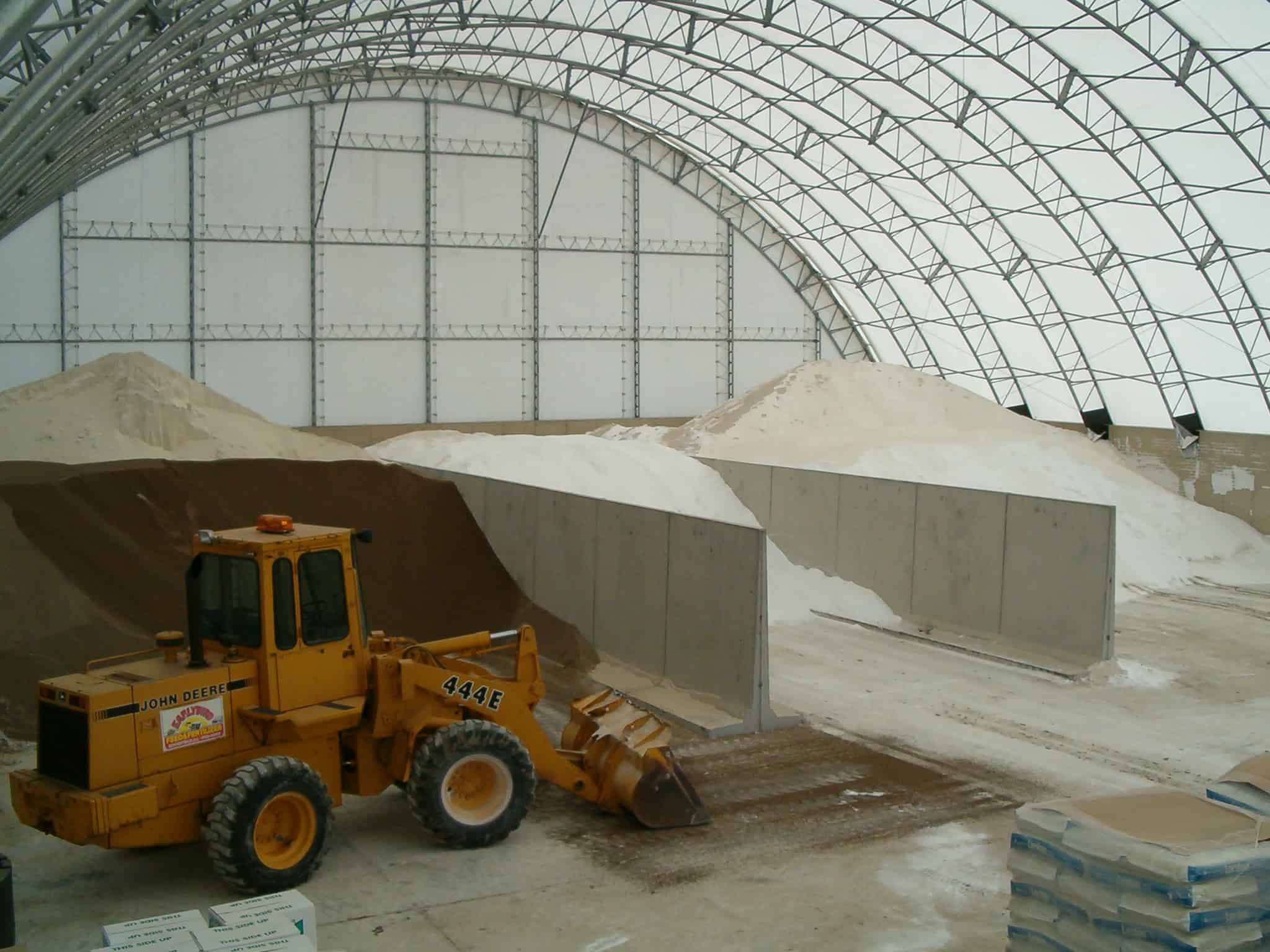

Image Credits: winklerstructures.com
- Entertainment Venues: Tensile architecture makes for an interesting exhibited venue for concerts or theatrical performances or even galleries. Large unobstructed spaces enable many different possibilities in terms of setup and lighting, improving the general attendees’ immersion.
- Educational Facilities: Temporary fabric structures are used in schools and other learning institutions that are cramped for space. They can be used as classrooms, gymnasiums or assembly halls to meet the student requirement where construction or remodeling is taking place.
- Research and Development: Temporary structures provide protected conditions for experiments and tests. They have full control of the lighting, temperature, and humidity to allow the creation of any environment required, and as such are perfect for research in agriculture, renewable energy, and material sciences.
- Vehicle Maintenance and Repairs: Tensile membrane structures can also give shelter for vehicles undergoing repair hence cutting down on time and protecting the machines from harsh weather. These structures can be provided with ventilation system and equipment hoist for easy repair works.
- Retail Spaces: Temporary structures made of fabric are especially common in pop-up shops, or temporary stores. They can be easily assembled having modular structure and provide companies with appealing promotional or seasonal spaces.
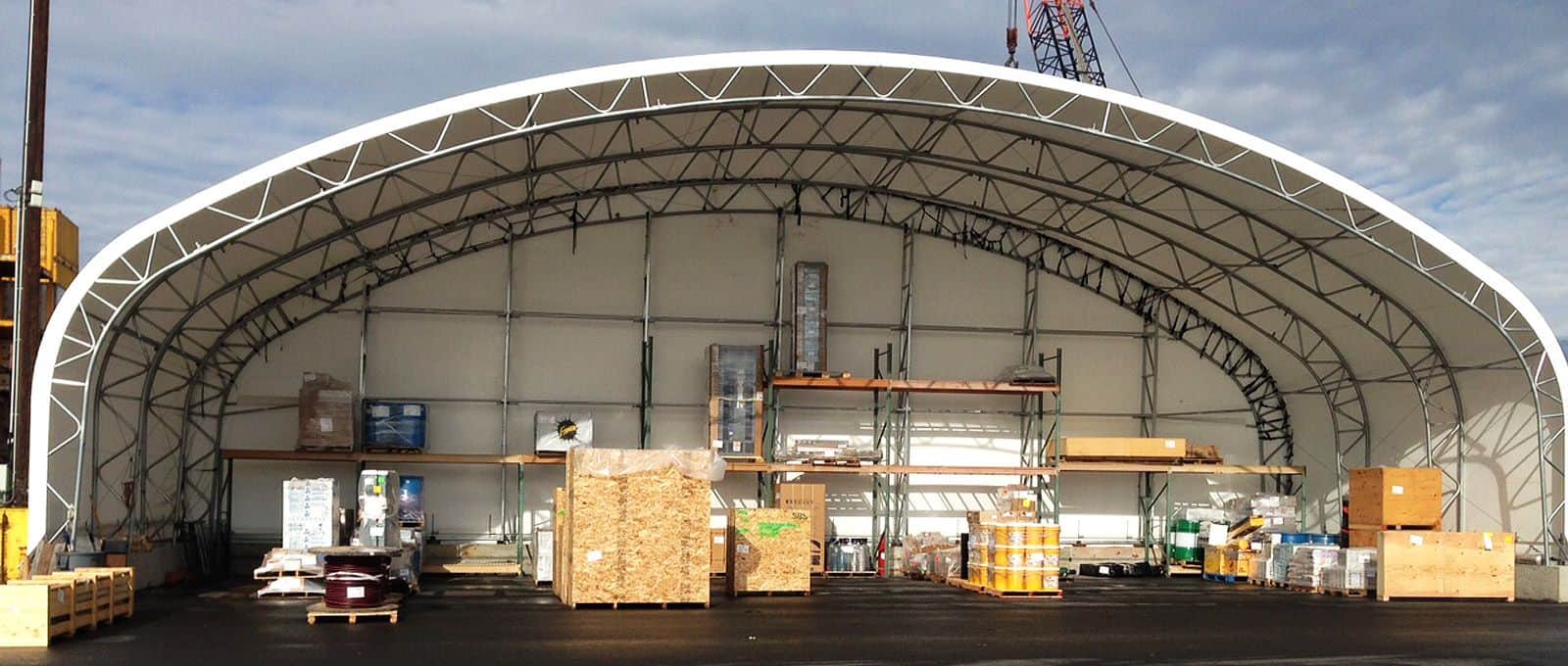

Image Credits: fabricstructures-usa.com
- Community Centers: Fabric structures provide excellent large span space for the purpose of group functions, production, and entertainment. These structures can be easily opened for various activities and enable the community to be bound together through the activities planned.
Benefits of Fabric Structures
1. Versatility
Fabric structures are extremely useful for a number of applications and for many types of industries. These can be applied for either short term or long term purposes. For example, they are often utilized as occasional structures, exhibition centers, and trade show structures. They also can serve as permanent structures such as sports facilities, concert halls, large warehouses, and factories.
2. Lightweight
Technologically advanced textile fabrics used in these structures are still lighter than normal construction materials such as steel, concrete or bricks. At the same time, this lightweight nature has several benefits. It cuts on the expenses of transport since lesser energy is used to transport the materials. Moreover, the construction of the structure also involves fewer uses of heavy machines and workforce, thus improving its efficiency in terms of expenses.
3. Aesthetics
The fabric based structures are aesthetically appealing and create a visually appealing sight. The flexibility of this material enables architects and designers to design complex, curvilinear and kinetic forms that can be challenging to realize in conventional construction materials. Such flexibility in aesthetic appearance may result in designs causing the building to be iconic and a landmark in the location.
4. Natural Lighting
Most fabrics used to construct these structures are transparent and allow natural light into the interior part of the building. This daylighting effect can provide a good and well lit environment where artificial light can hardly be needed during the day.
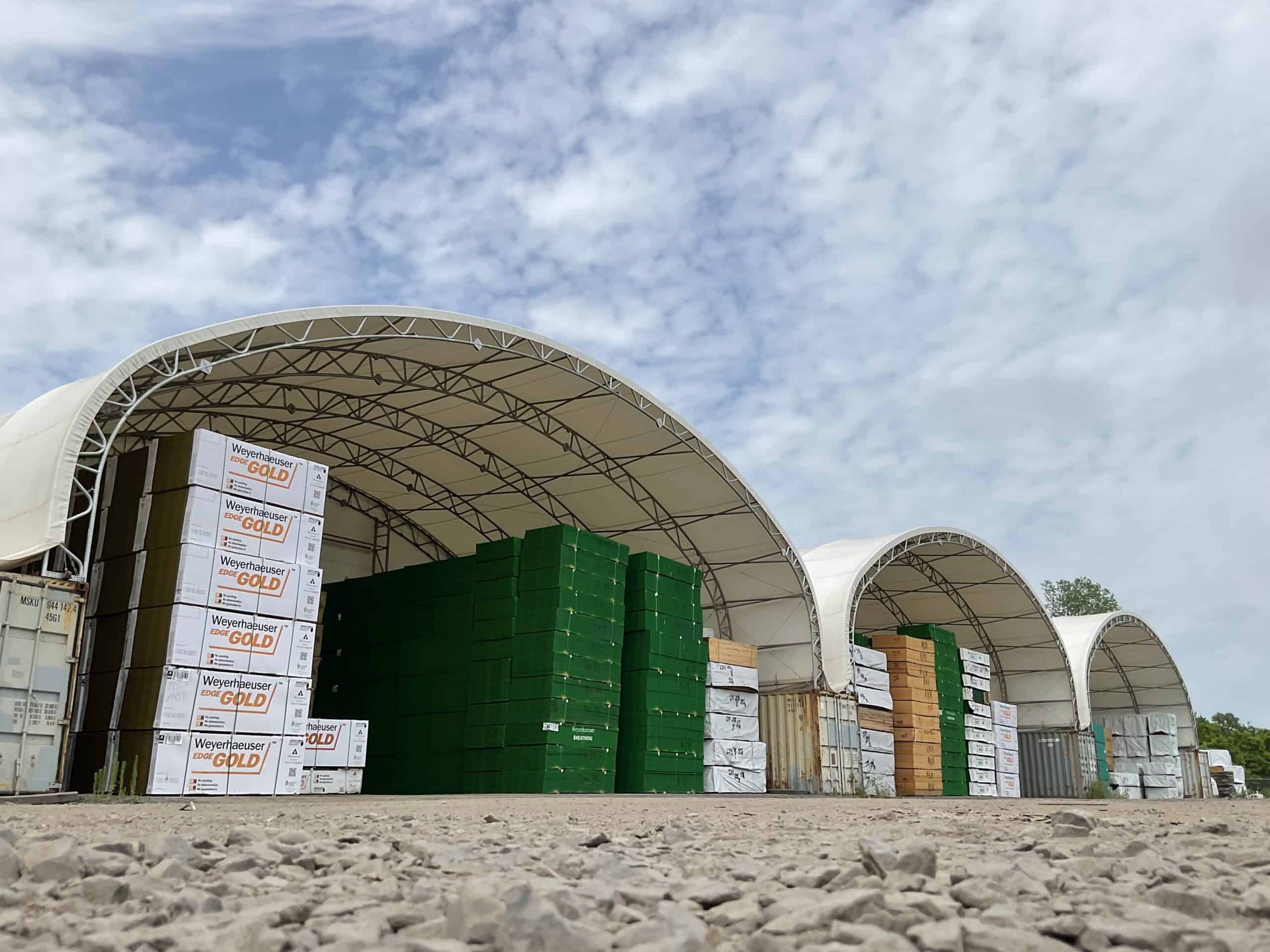

Image Credits: bigtopshelters.com
Consequently, the energy utilization is reduced, while the inhabitants gain a healthier and more comfortable environment.
5. Quick Installation
Compared to conventional construction, fabric structures can be erected in a relatively short amount of time. This is because most of the components are manufactured then transported to be assembled at the site of the building. This is especially beneficial for situations or projects that can only be done quickly before a shelter is necessary.
6. Cost-Effectiveness
The combination of lightweight materials, quicker installation times, and reduced labor requirements contributes to cost savings. Fabric structures can be a more economical choice, especially for temporary or semi-permanent applications. They can sometimes be more financially viable than constructing a traditional building.
7. Customization
Fabric structures can come in various designs depending on the function and aesthetics that are desired.
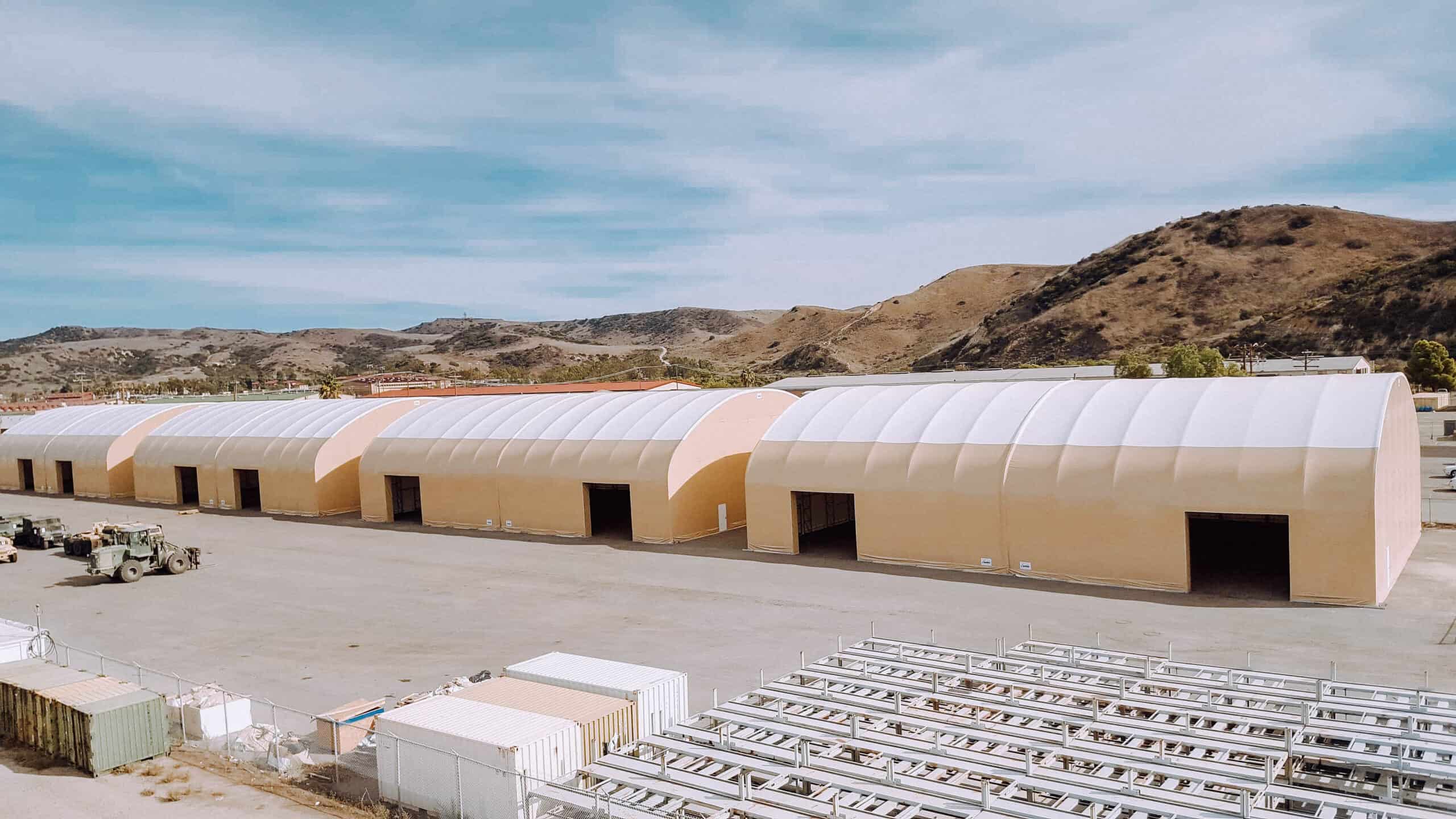

Image Credits: bigtopshelters.com
The shape, size, and color can be used in various ways to ensure that the architects deliver the desired solutions that meet the clients’ needs and requirements. Such customization leads to the formation of differentiated and therefore, easy-to-remember places.
8. Low Maintenance
Most fabric materials applied in these structures are made to be resistant to wear and tear and conditions such as Ultra-Violet radiation, moisture as well as fire. This inherent characteristic also means that it would not require constant maintenance over time and fewer costs in maintaining the building.
9. Sustainability
There are specific fabrics that are environmental friendly and contribute to lesser emissions of carbon than other construction materials.
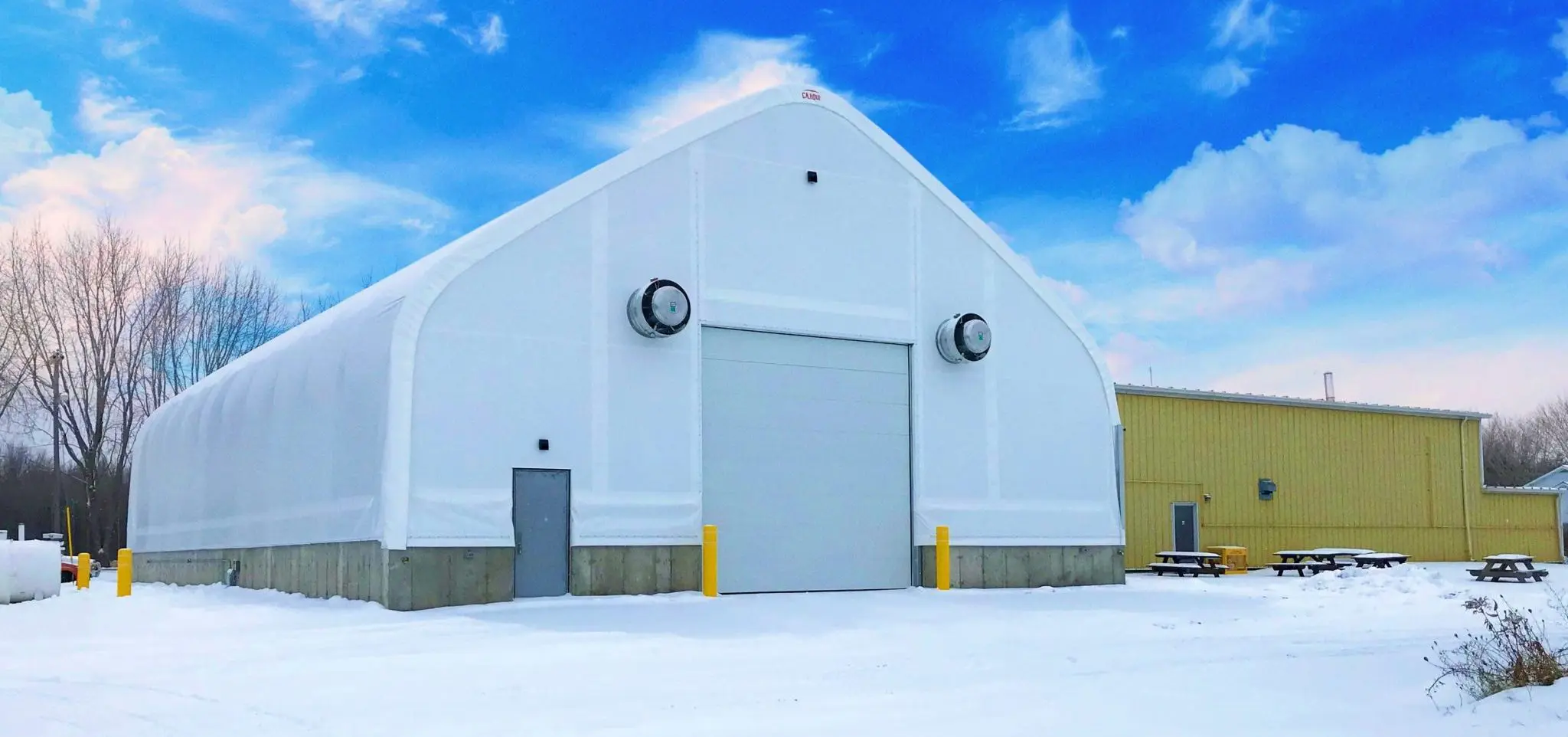

Image Credits: calhounsuperstructure.com
The admission of natural light through these materials eliminates the need for artificial lighting hence conserving energy. Also, some fabrics are recyclable, which makes the construction process more environmentally friendly.
10. Flexibility and Portability
It is possible to dismantle fabric structures, transport them to another area or use them for another purpose, which makes them very flexible. This characteristic makes it ideal when there are short term usage or when the structure needs to change from one use from another depending on the prevailing circumstances.
11. Noise Absorption
Some of the fabric materials have the ability to absorb sound. This makes fabric structures ideal for areas where sound insulation is vital, for example, concert halls, theatres or event spaces.
12. Expansion and Adaptation
Fabric structures can be easily extended or altered by adding or deleting modules. This versatility makes it possible for organizations or businesses to change the size and design of the structure in relation to how it is being used.
Frequently Asked Questions On Fabric Buildings
1. What are fabric buildings?
Fabric structures encompass a fabric or membrane that is tightly drawn and supported with steel or aluminum frames. Some fabrics can be sprayed with PVC or polyethylene to enhance their ability to resist weather elements. Temporary or semi permanent structures like a warehouse, a sports center or an agricultural storage usually take benefits of fabric structures since these are comparatively less expensive and less time taking to construct as compared with traditional constructions. They are versatile in design and can be adopted in many ways depending on the requirements.
2. What is the function of fabric building?
Fabric structures are used for several reasons; they act as temporary or semi permanent structures mainly for industrial, agricultural, recreational and commercial purposes. Being constructed from a fabric stretched on a frame they also enable fast, cheap and easily installable solution for storage, events or sports. The fabric material can withstand different weather conditions making it possible to use the structure in different weather conditions.
3. What are the benefits of fabric buildings?
Fabric structures are cheaper, installation is fast, and they can be made in any design. They are used more frequently in temporary or semipermanent constructions; they help to solve many problems. Fabric material that is common may also be durable and is sometimes weather resistant. They are also known for their energy use efficiency, for instance, in that they can be designed to admit natural light, thus limiting artificial lighting. Due to their relatively small mass and versatility, they are used in various fields.
4. How long do fabric buildings last?
Fabric structures generally have a lifespan ranging from 15 to 25 years based on the used fabric material and the surrounding environment it is subjected to. It should, however, be noted that they can be made to last longer through proper maintenance. It is for this reason that the fabric covering may require replacement more frequently than the frame, which usually tends to be more resilient. Lifespan is relative to usage and manufacturer-recommended time frame for the usage of the item.
Conclusion
Fabric structures combine aesthetics, technology and environmental concerns. They expand the architectural possibilities and give answers that are flexible, meaningful, and sometimes more in harmony with the environment.
The opportunity for innovation lies in its future, as new technologies are expected to improve the construction of fabrics and the properties of buildings. Looking at today’s construction, fabric buildings are essential in promoting the growth of our environment.
It is not all gloomy news, though; the potential is enormous. From a historical perspective and future potential, they are an impressive example of a human ability to create fabric structures as shelters with outstanding properties. From sports stadiums to mobile shelters, the possibilities of fabric structures are endless and bound only by the prospectus of architectural innovation.